|
Cybernetics and Linguistics
|
The Scientific
contemplation of Nature makes two distinctions in the building of life
and its industry: Life carries a meaning process, as it is shown
through languages, behaviors and instincts - it is also called 'system of value'
- and it also carries sequencing
of code, social, chemical, genetic for example. Significand (meanings)
and Code (registration) are correspondent but different. Both their domains are intertwined and
often overlap - yet they can be differentiated
through their logic.
|
A General example
 It is important to appreciate
under which condition the distinction between Code and Significand happens
in the human thinking, otherwise we would not be able, as human, to use
it efficiently. It is important to appreciate
under which condition the distinction between Code and Significand happens
in the human thinking, otherwise we would not be able, as human, to use
it efficiently.
 The human brain does not make
distinction between phenomena, unless it is imposed upon its perception. The discrimination between
the two Code and Significant logics has been brought to our perception
through the effects of the
modern Information Technology and its science which is Cybernetics. Beside
covering the fields of electronics, Information Technology, network systems,
Artificial Intelligence, robotics etc... as the science of the relationship
between artificial systems and nature, Cybernetics has imposed the need for
discriminating a relationship between data and meaning
(sometime also called meta-data) of information itself. Important
enough, this discrimination allows an identification within an environment. The human brain does not make
distinction between phenomena, unless it is imposed upon its perception. The discrimination between
the two Code and Significant logics has been brought to our perception
through the effects of the
modern Information Technology and its science which is Cybernetics. Beside
covering the fields of electronics, Information Technology, network systems,
Artificial Intelligence, robotics etc... as the science of the relationship
between artificial systems and nature, Cybernetics has imposed the need for
discriminating a relationship between data and meaning
(sometime also called meta-data) of information itself. Important
enough, this discrimination allows an identification within an environment.
 Data and Meaning constitute
our current Knowledge. If the Cybernetic degree of our present technology would
collapse tomorrow, this actual form of our Knowledge would probably be the
next thing to vanish. Admitting that our actual Knowledge is an outcome of Cybernetics,
as a modern subject admits that he or she is the outcome of an Unconscious,
keeps us realistic and efficient, with a constant awareness that the role
and function of the Cybernetic apparatus in society will always be included
in all account and definition of knowledge. A recent example will make
our point explicit: Data and Meaning constitute
our current Knowledge. If the Cybernetic degree of our present technology would
collapse tomorrow, this actual form of our Knowledge would probably be the
next thing to vanish. Admitting that our actual Knowledge is an outcome of Cybernetics,
as a modern subject admits that he or she is the outcome of an Unconscious,
keeps us realistic and efficient, with a constant awareness that the role
and function of the Cybernetic apparatus in society will always be included
in all account and definition of knowledge. A recent example will make
our point explicit:
 Government, Academia, Business
and Industry are currently compelled to identify what librarians call Grey
Literature (that is the unregistered textuality: pre-print, email, Web
etc... in comparison with a 'White' Literature which represents the official
and published documents). They thus actualize a 'Tacit Knowledge'
beside an 'Explicit Knowledge' (this can be found in any glossary of Knowledge Management). All
observers agree that this identification is made necessary
by Cybernetics (Information Technology: Internet, electronic networks etc...).
Before this effective Cybernetics, nobody was interested by the distinction
between Grey and White literature. It was not factual. The reality is that
it came to the human mind and collectively, under the pressure of Cybernetics;
and it would lead to a catastrophe if the role of Cybernetics was not constantly
kept acknowledged along with its management. Psychoanalysis describes how the
oblivion of a causal factor of our perception elaborates a Death Drive (Thanatos). Government, Academia, Business
and Industry are currently compelled to identify what librarians call Grey
Literature (that is the unregistered textuality: pre-print, email, Web
etc... in comparison with a 'White' Literature which represents the official
and published documents). They thus actualize a 'Tacit Knowledge'
beside an 'Explicit Knowledge' (this can be found in any glossary of Knowledge Management). All
observers agree that this identification is made necessary
by Cybernetics (Information Technology: Internet, electronic networks etc...).
Before this effective Cybernetics, nobody was interested by the distinction
between Grey and White literature. It was not factual. The reality is that
it came to the human mind and collectively, under the pressure of Cybernetics;
and it would lead to a catastrophe if the role of Cybernetics was not constantly
kept acknowledged along with its management. Psychoanalysis describes how the
oblivion of a causal factor of our perception elaborates a Death Drive (Thanatos).
 On the opposite, when we admit the
necessity to count Cybernetics
as a real factor of our actual Knowledge, we observe and study it,
and realize that such acknowledged intervention of Cybernetics within the Significand
space (Literature) causes a regeneration of the Code (organization). This
has been described within the context of Literature.
It is what we shall look more in depth in the scope of general Knowledge. On the opposite, when we admit the
necessity to count Cybernetics
as a real factor of our actual Knowledge, we observe and study it,
and realize that such acknowledged intervention of Cybernetics within the Significand
space (Literature) causes a regeneration of the Code (organization). This
has been described within the context of Literature.
It is what we shall look more in depth in the scope of general Knowledge.
 Or
first observation is that the
distinction between data and meaning gets more refined as distinction between
Code and Significand: Or
first observation is that the
distinction between data and meaning gets more refined as distinction between
Code and Significand:
The Code:
 The system of the Code is made
of items which represent something for other things (examples: in
a computer, a code represents a command for a key-board button; in society
and profession, a code represents a salary for a certain job production). This
can be formulated according to the linguistic mode of representation - by conventions in Linguistic algorithms, the
Code (item 'C') is
above and separated by a trait from a certain thing 'x1', meaning that it 'represents'
x1 for another thing, x2 : The system of the Code is made
of items which represent something for other things (examples: in
a computer, a code represents a command for a key-board button; in society
and profession, a code represents a salary for a certain job production). This
can be formulated according to the linguistic mode of representation - by conventions in Linguistic algorithms, the
Code (item 'C') is
above and separated by a trait from a certain thing 'x1', meaning that it 'represents'
x1 for another thing, x2 :
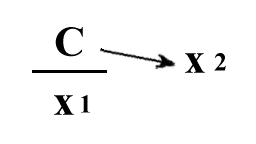
Fig 01: formula of the Code
A three places - tripartite topology
 First we see this algorithm as
representing data (for example, a certain number, C, represents a certain length, x1). But it reveals data's more complex nature that we believe
at first sight. For instance, the length of an artifact does not stand
by itself, it is relative and if must be referred. For their practicability,
data are built according on a principle of code - for an example: a centimeter ('x1') represents something for a metric system ('x2'). First we see this algorithm as
representing data (for example, a certain number, C, represents a certain length, x1). But it reveals data's more complex nature that we believe
at first sight. For instance, the length of an artifact does not stand
by itself, it is relative and if must be referred. For their practicability,
data are built according on a principle of code - for an example: a centimeter ('x1') represents something for a metric system ('x2').
 An important development results
from the awareness of a Structure of Code at the base of our perception: An important development results
from the awareness of a Structure of Code at the base of our perception:
 Further analysis of this algorithm
shows that such simple, yet trine and primary complex ('C', 'x1', 'x2'), generates a logic
which superdetermine the Code itself and its items (order of increment
for example). In certain environment this superdetermination can become
quite complex (genetic code for example) and constitutes a logic by itself.
Hence, beyond a structure of Code, a logic of Code must be made part of
our knowledge. Further analysis of this algorithm
shows that such simple, yet trine and primary complex ('C', 'x1', 'x2'), generates a logic
which superdetermine the Code itself and its items (order of increment
for example). In certain environment this superdetermination can become
quite complex (genetic code for example) and constitutes a logic by itself.
Hence, beyond a structure of Code, a logic of Code must be made part of
our knowledge.
 This logic has been called a Serial
Logic, while such description and awareness of the Code has
followed the progress of the modern age: This logic has been called a Serial
Logic, while such description and awareness of the Code has
followed the progress of the modern age:
|
The serial logic has been grounded on
Sociology:
 The premises of
a described Logic of Code can be found in the concluding
philosophy of Friedrich Hegel. The initiation of
Cybernetics had been laid earlier, in the last moments of the Hermetic
Tradition along with its repression (Note10). And
though Hegel was participating with the beginning of the Era of Masses,
Cybernetics was not yet apparent in his time in order to practically
ground his conceptualization. Later, his follower Jean-Paul.Sartre is
still known as a philosopher. But if Sartre could refuse the
Nobel Price at the end of his life, this is nevertheless strongly
indicating the scientific quality of his writings on Sociology.
Actually, improving the knowledge of his time according to the Hegelian phenomenology, he participated in the electronic age and coined a Serial Logic
which has been then implemented by his disciple, the English
Psychiatrist Ronald D.Laing, with a complete formulation in a social
Psychiatry. From that moment, the Serial Logic was brought very close to
the fields of social perception, mentalities, beliefs and knowledge; and
ready to ground a theory of Code. The premises of
a described Logic of Code can be found in the concluding
philosophy of Friedrich Hegel. The initiation of
Cybernetics had been laid earlier, in the last moments of the Hermetic
Tradition along with its repression (Note10). And
though Hegel was participating with the beginning of the Era of Masses,
Cybernetics was not yet apparent in his time in order to practically
ground his conceptualization. Later, his follower Jean-Paul.Sartre is
still known as a philosopher. But if Sartre could refuse the
Nobel Price at the end of his life, this is nevertheless strongly
indicating the scientific quality of his writings on Sociology.
Actually, improving the knowledge of his time according to the Hegelian phenomenology, he participated in the electronic age and coined a Serial Logic
which has been then implemented by his disciple, the English
Psychiatrist Ronald D.Laing, with a complete formulation in a social
Psychiatry. From that moment, the Serial Logic was brought very close to
the fields of social perception, mentalities, beliefs and knowledge; and
ready to ground a theory of Code.
 The achieved
step has been made with the junction of this serial logic of Code, with
another logic - namely of the Significand - which is the Science of
Meaning, and which was described concurrently by Psychoanalysis. The achieved
step has been made with the junction of this serial logic of Code, with
another logic - namely of the Significand - which is the Science of
Meaning, and which was described concurrently by Psychoanalysis.
|
The Significand:
 A scientific concept of Significand
originated with Linguistics at the end of the 19th Century (Ferdinand de
Saussure) - it has been then applied and improved by the Psychoanalyst
Jacques Lacan. In 1960 Lacan attempted to formulate Freud's
still intuitive concept of the Unconscious. He elaborated a degree of algebra
using the Saussurian foundation. In Lacan's algorithms 'Knowledge'
is explicitly represented by the symbol S2. A scientific concept of Significand
originated with Linguistics at the end of the 19th Century (Ferdinand de
Saussure) - it has been then applied and improved by the Psychoanalyst
Jacques Lacan. In 1960 Lacan attempted to formulate Freud's
still intuitive concept of the Unconscious. He elaborated a degree of algebra
using the Saussurian foundation. In Lacan's algorithms 'Knowledge'
is explicitly represented by the symbol S2.
 The idea of De Saussure have
been that the objects of Linguistics, the signifier or 'Significand' differed
from a code in that they were representing something for another Significand
(instead of another thing). Beside the algorithm of Code, a second algorithm
can thus be written: The idea of De Saussure have
been that the objects of Linguistics, the signifier or 'Significand' differed
from a code in that they were representing something for another Significand
(instead of another thing). Beside the algorithm of Code, a second algorithm
can thus be written:
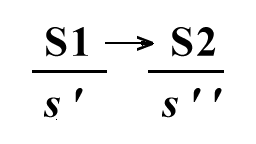
Fig 02: formula of the Significand
A four places - quadripartite topology
 The algorithm of the Significand
indicates that a 'first' Significand (S1) implies another one, which represents
its knowledge (S2). This is ruling a different logic that of the Code.
This Lacanian formula shows that this logic (S1;S2) has shifted above
the signified (s', s'', s'''...), of which it appears to become independent. In
the personal human experience, this is manifested through the feeling of independence
of thoughts. In the field of science, such shift implies an improvement,
as it allows to formulate knowledge, yet
a loss at the same time, for it generates an industry that can apparently lose all contact with reality
(the signified). Two examples can illustrate this situation:
it is the case when an Operating System allows software to communicate
together without bound to their underlying hardware. As a biological example,
it is the situation which allow dreams. The algorithm of the Significand
indicates that a 'first' Significand (S1) implies another one, which represents
its knowledge (S2). This is ruling a different logic that of the Code.
This Lacanian formula shows that this logic (S1;S2) has shifted above
the signified (s', s'', s'''...), of which it appears to become independent. In
the personal human experience, this is manifested through the feeling of independence
of thoughts. In the field of science, such shift implies an improvement,
as it allows to formulate knowledge, yet
a loss at the same time, for it generates an industry that can apparently lose all contact with reality
(the signified). Two examples can illustrate this situation:
it is the case when an Operating System allows software to communicate
together without bound to their underlying hardware. As a biological example,
it is the situation which allow dreams.
|
The Logic of the Significant has been grounded on
Sociology:
 During the 20ht century a major
expression of this logic as been described by Sociology. It is Emile
Durkheim in Europe, who suggested that the organization of Society was
less directed by an apparent ideal or by direct material inductions, than
driven by the plurality of meanings which were manifested as professions
and roles (Division of Labor). These building blocks of the social world cannot stand alone,
one by one. For instance the industry of iron extraction has no meaning
without the industry of blacksmith, which has no meaning without industry
of fire and also mechanics, architecture etc... In a society which is based on
a 'Division of Labor', each primary item stands only in regard of at least
another one. The model of Linguistics thus applies to the Western Sociology,
whose Industry forms discourses which operates in the environment as a language. During the 20ht century a major
expression of this logic as been described by Sociology. It is Emile
Durkheim in Europe, who suggested that the organization of Society was
less directed by an apparent ideal or by direct material inductions, than
driven by the plurality of meanings which were manifested as professions
and roles (Division of Labor). These building blocks of the social world cannot stand alone,
one by one. For instance the industry of iron extraction has no meaning
without the industry of blacksmith, which has no meaning without industry
of fire and also mechanics, architecture etc... In a society which is based on
a 'Division of Labor', each primary item stands only in regard of at least
another one. The model of Linguistics thus applies to the Western Sociology,
whose Industry forms discourses which operates in the environment as a language.
|
|
Code and Significand constitute the two logics which combine to make
Cybernetics.
We have also noticed twice that these two logics are related
to a social dimension.
This will fulfill the requirement that Cybernetics,
as we want to keep it present in our formulation of Knowledge,
indicates
its acquaintance with the social dimension.
Hence it is necessary and time to see why and how
the ground of sociology reciprocally calls for, and needs to absorb
the factor of Cybernetics
|
|





![]() This article describes how the
Science of Representations and Meanings, known as Linguistics, stresses
and reduces two major notions (Information Technology and Knowledge Management)
as two redundancies, meaning that Technology is Information, and
its Management is Knowledge. This treatment of our concepts
is a management itself - that is knowledge which is expressed in algebraic
formulae.
This article describes how the
Science of Representations and Meanings, known as Linguistics, stresses
and reduces two major notions (Information Technology and Knowledge Management)
as two redundancies, meaning that Technology is Information, and
its Management is Knowledge. This treatment of our concepts
is a management itself - that is knowledge which is expressed in algebraic
formulae.